GENERAL ORGANISATION AND CHARACTERS OF VIRUSES (HEPATITIS B VIRUS AND SARS COV-2)
INTRODUCTION
Viruses are very small submicroscopic biological entities which though lack plasma membrane and metabolic machinery. Viruses require some host cell that is they are obligate cellular parasites of either bacteria, plants or animals. There genetic material is can be RNA or DNA.

TYPES OF VIRUSES
A. Bacteriophages or Bacterial viruses : viruses whose host are bacterial cells, are called bacteriophages or phages ( ‘phage means to eat’). These bacteriophages have specific hosts and have variable shapes, sizes and structures. Examples- T-even bacteriophages such as T2, T4, T6, etc., which infect E. Coli ( Escherichia coli) and are also known as coliphages. T4 bacteriophage is a large- sized viruses. It’s shape is tadpoles like. It has head, short neck with ‘whiskers’ and a long tail. The end plate in the end have six spikes and six long tail fibres.
B. Plant viruses : Viruses whose host are plant cells and disturb their metabolism and cause severe disease in them. Plant viruses have ribonucleoproteins in their organization. Examples are tobacco rattle virus (TRV), tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), potato virus etc. The diseases caused are mosaic diseases of tobacco, cabbage, cauliflower; black-ring spot of cabbage; leaf roll of tomato; leaf curl of papaya. These diseases are spread mainly by insects such as aphids, leaf hoppers and beetles. TMV is a rod-shaped, helically symmetrical RNA virus.
C. Animal Viruses : The animal viruses infect the animal cells and cause different fatal diseases in animals including animals. They are polyhedron or spherical in shape and genetic material in the form of DNA or RNA. Examples – influenza, herpes simplex, viral encephalitis, and some types of cancer.
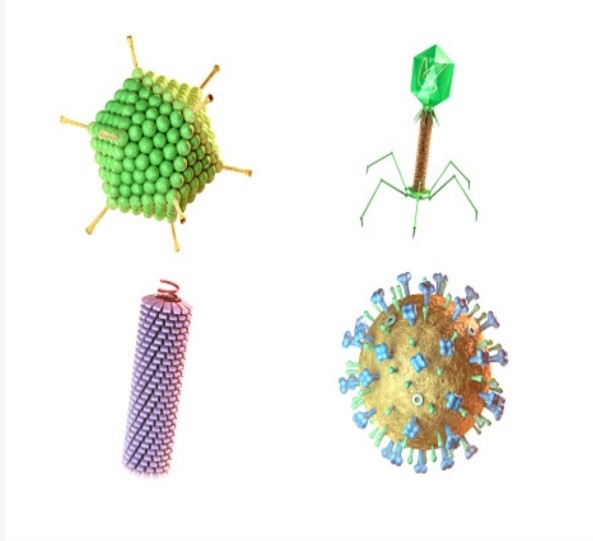
STRUCTURE OF VIRUSES
- The size of viruses varies from 30 to 300nm , so they can be observed only by electron microscopy and X Ray crystallography.
- Viruses have only one kind of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA).
- Covered with a protective coat of protein, called
- Capsid = capsomeres each having monomers or structural units.
- Capsomeres are of different shapes such as hollow prism, hexagonal, personal, globular or any other shape.
Viruses have the following three types of symmetry :
- Icosahedral symmetry- many viruses have spherical, cubical or polygonl shape which is basically icosahedral or 20-sided. Icosahedral capsid comprises of pentameres which have five structural units and hexameres which have 6 structural units.
For example:
- Bacteriophages phi×174= 12 pentameres
- TYMV (turnip yellow mosaic virus) = 32 capsomeres
- Poliovirus =32 capsomeres
- Reovirus = 92 capsomeres
- Herpes virus= 162 capsomeres
- Helical or cylindrical symmetry- The rod shaped helical capsid of viruses which as tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), bacteriophages M13 and influenza virus, have numerous identical capsomeres arranged in a helix.
- Complex symmetry- these are of two shapes, first those without identifiable capsids Example pox viruses such as vaccinia, cowpox etc. and those with tadpole shaped structure, e.g., T-even phages of E-coli.
CHARACTERS OF VIRUSES
- They lack plasma membrane.
- Deluxe cytoplasm and metabolic machinery.
- There are living and nonliving characters in virus
- Living characters of viruses
- Viruses have the capacity to multiply.
- They have the property of undergoing mutations.
- They have the property of recombination and inheritability.
- Non living characters of viruses
- Viruses have the property of crystallization
- They lack enzyme system.
- They lack response to external stimuli.
- They lack growth.
EXAMPLES OF VIRUSRS
HEPATITIS-B
- Hepatitis B virus have features similar to retroviruses.
- It is a small partially double stranded DNA virus.
- It causes hepatitis-B disease
- Member of hepadnavirus family.
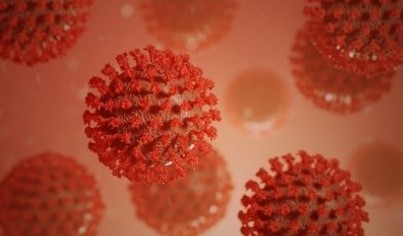
SARS CoV-2
- Member of coronaviruses.
- SARS CoV-2 is a virus that causes a respiratory disease called corona virus 19 disease.
- It is unsegmented single stranded RNA virus .
- 26 to 32Kb in length.
CONCLUSION
Viruses are submicroscopic organisms having RNA or DNA as genetic material. Viruses are divided into 3 types based on the type of host they attack, bacteriophages, plant viruses and animal viruses. Shapes and structure of viruses varies greatly. On the basis of symmetry of capsid they are mainly of Icosahedral, helical and complex symmetry.
Share this:
- Post
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window) Email
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window) Reddit
- Tweet
- Share on Tumblr
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window) Telegram
- Click to share on Threads (Opens in new window) Threads
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window) WhatsApp
- Click to share on Mastodon (Opens in new window) Mastodon
- Click to share on Nextdoor (Opens in new window) Nextdoor
- Click to print (Opens in new window) Print
- Click to share on Bluesky (Opens in new window) Bluesky
Related
Discover more from ZOOLOGYTALKS
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


Pingback: Human papillomavirus (HPV) | ZOOLOGYTALKS | 2021